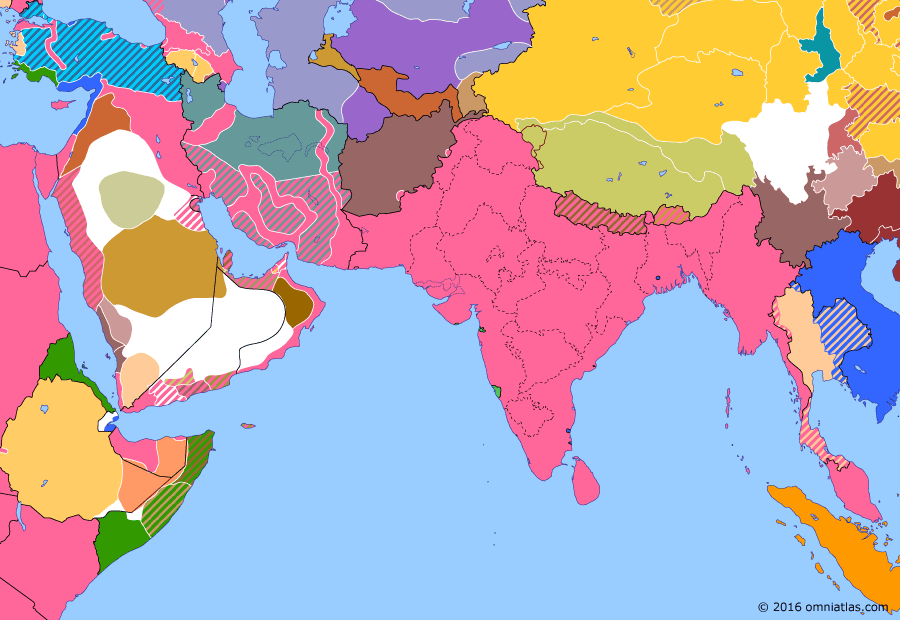
Southern Asia 1919: Third Anglo-Afghan War
11 June 1919
11 Jun 1919
Anglo-French Overreach
1880–1914 Pax Britannica
1914–1917 Great War in the Middle East
1917–1918 Fall of the Ottoman Empire
1918–1923 Anglo-French Overreach
1923–1934 Rising Nationalism
1934–1940 Arrival of the New Order
1940–1941 World War II: The Middle Eastern Theater
1941–1945 World War II: The South-East Asian Theater
1945–pres Independence
Third Anglo-Afghan War
13 Apr 1919 Amritsar Massacre
11 Jun 1919 Third Anglo-Afghan War
9 Aug 1919 Anglo-Persian Agreement
27 Dec 1919 Turkish War of Independence
18 May 1920 Soviet Victory in Central Asia
25 Jul 1920 Franco-Syrian War
10 Aug 1920 Treaty of Sèvres
28 Nov 1920 Turkish-Armenian War
5 Apr 1921 Rise of Reza Khan
27 Aug 1921 Greco-Turkish War
5 May 1922 Saudi Expansion
8 Sep 1922 Turkish Great Offensive
2 Dec 1922 Uqair Protocol
The unrest in India around the Amritsar massacre encouraged Afghanistan to assert itself against Britain. In May 1919 it invaded northern India, but was rapidly pushed back by the British. Nonetheless, in the ensuing peace treaty, Britain agreed to recognize Afghanistan as a fully independent state.