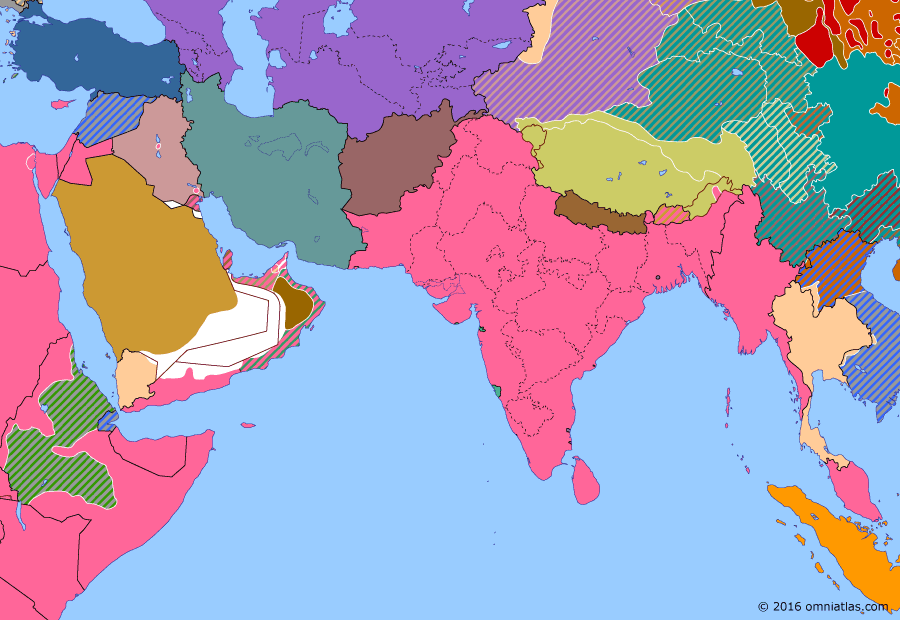
Southern Asia 1941: Liquidation of Italian East Africa
6 April 1941
6 Apr 1941
World War II: The Middle Eastern Theater
1880–1914 Pax Britannica
1914–1917 Great War in the Middle East
1917–1918 Fall of the Ottoman Empire
1918–1923 Anglo-French Overreach
1923–1934 Rising Nationalism
1934–1940 Arrival of the New Order
1940–1941 World War II: The Middle Eastern Theater
1941–1945 World War II: The South-East Asian Theater
1945–pres Independence
Liquidation of Italian East Africa
The British conquest of Italian East Africa culminated with the Italian surrender of Addis Ababa on 6 April 1941. One month later, Emperor Haile Selassie returned to his capital in triumph, marking the symbolic restoration of the Ethiopian Empire. However the Italian army would continue to hold out in the interior until November, with guerrilla warfare carrying on even after that.