Asia Pacific 1914: Conquest of the German Pacific
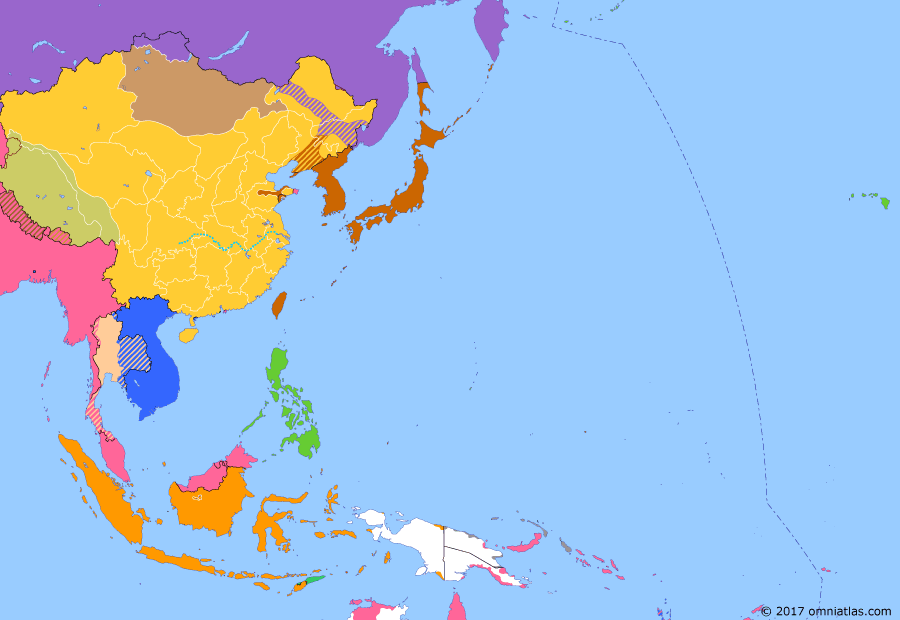
10 October 1914
10 Oct 1914
Conquest of the German Pacific
6 Dec 1911 Chinese Revolution
10 Mar 1912 Yuan Shikai and the Republic of China
28 Jul 1913 Second Chinese Revolution
10 Oct 1914 Conquest of the German Pacific
18 Jan 1915 Japan's Twenty-One Demands
6 Jun 1916 China's Warlord Era Begins
15 Dec 1917 Russian Revolution
31 Aug 1918 Siberian Intervention
4 May 1919 May Fourth Movement
6 Apr 1920 Creation of the Far Eastern Republic
23 Jul 1920 Zhili–Anhui War
25 Jun 1921 Russia in Mongolia
6 Feb 1922 Washington Naval Conference
30 Dec 1922 Japanese Withdrawal
23 Oct 1924 Beijing Coup
30 May 1925 Shanghai Incident
24 Apr 1926 Anti-Fengtian War
When World War I broke out in Europe, the Anglo-Japanese Alliance meant that Japan sided with the British against Germany. Together with the British dominions of Australia and New Zealand, the Japanese quickly conquered Germany's Pacific empire.